Embryo Transfer Technology | Complete Procedure
It is also called ovum transfer. It is the collection of fertilized ovum from the donor prior to its attachment/nidation with uterus and transfer into surrogative/recipient mother for completion of gestation period.
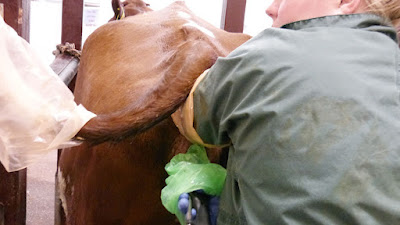 |
| Oocyte collection |
The cow from which we get the embryo is called as donor. The cow to which we transfer embryo is called recipient. In AI, semen is inseminated in different cows; the genetic potential of male is distributed which is same for all cows but different cows have different potential. In embryo transfer, genetic potential of female is distributed.
Every cow produces one egg at the time of estrus. Donor cows are induced to produce more than one egg at the time of estrus. These eggs are inseminated and then these fertilized eggs/embryos are taken from donor. At the same time recipient cows, having low genetic potential, are also prepared and one embryo is placed in each cow. In this way more than one calf can be obtained from one donor.
Advantages of Embryo Transfer:
- It improves the genetic potential
- It increases the productivity
- It increases the economic benefit
- It increases the disease resistance
- It increases the no. of calves in life time
- It reduces the generation interval
- It increases the selection intensity
- Import and export is easier because it is done in the form of embryo in which transportation is easier, genetics is diversified, and cost is decreased.
- Selection of donor
- Selection of recipient
- Synchronization of donor and recipient
- Superovulation of donor
- Insemination of donor
- Collection of embryos
- Evaluation of embryos
- Transfer or storage of embryos.
- It should be from known fertile blood line i.e. we must have pedigree record
- It should have calved once earlier so heifer as a donor is not required.
- Donor should have known calving history or easy calving history.
- It should be a regular cyclic animal.
- It should be a disease free animal e.g. T.B, brucellosis
- It should have been vaccinated
- It should be high producing and reproduction wise normal
d1 d6 d11 d14 d17
Estrus: ∙----------∙----------∙------∙------∙
CL PGF2α Heat
d1 d3 d9 d11 d14 d17
Proestrus: ∙----∙------------∙----∙------∙------∙
Heat CL PGF2α Heat
d1 d4 d11 d14 d15
Metestrus: ∙------∙--------------∙------∙--∙
CL PGF2α Heat
d1 d3 d9 d11 d14 d20
Diestrus: ∙----∙------------∙----∙------∙------------∙
PGF2α Heat CL PGF2α Heat
Animal in estrus do not have any CL. 6 days later there will be CL. This CL will persist for 11-17 days.
Proestrous animal comes in estrus after one or two days. They do not have CL. So no response of PGF2α on day third. On day 9, CL will present which remain for day 20.
Metestrus animal was in estrus two days earlier. On day four CL will be formed which stays in ovary till day 15.
In diestrus animal has functional CL. Give PG on first day, on day 3 they come in heat. They will develop CL on ovary on day 9. 6 days will be taken by CL to develop. On day 20 CL will persist.
Anestroue do not respond to any one.
Insemination of Donor
Inseminate donor in standing heat. Inseminate two or three times after twelve hours and each time go for double dose.
Collection of Embryo
Until 1975, embryos were collected surgically. After anesthesia (general or local), entering the uterus and collect embryos. It was very difficult to collect from donors at farm. The cost of collection was too much. Another problem was, some damage may lead to future adhesion in reproduction tract. People tried to collect without surgery.
Non surgical method is preferable now because there is no damage or very little damage that provides repeatability for the donor to donate embryos and made collection at farm level possible. Disadvantage of this method is that we can only collect the embryo when it enters the uterus. But with surgery we can collect embryos while they are in oviduct.
Procedure of Collection:
- Place the donor in crushes, wash the perennial region. Evacuate rectum from feces and evaluate no. of CL on both ovaries, it will tell the no. of embryos. Older cows suck air in rectum and uterus, so very old cows are not used but if they are good we can use them. Apply a bally band that would create a positive pressure instead of negative pressure.
- Apply epidural anesthesia to decrease the movements in cow. Collection is done with the help of catheter. Three kinds of catheters are used; most commonly used is Foley’s Catheter. It could be two ways or three ways.
- It is easily available and inexpensive also. It is soft in nature. In surgery we clamp the uterus horns and throw fluid inside and suck it again which will contain embryos. In non surgical collection we have to fix catheter in uterus horn in a method that embryos cannot pass out of horn into uterus and portion is blocked completely. There are two methods:
- Continuous Flow Method: There is less loss of fluid but there are a lot of tubes that we have to handle. It may cause contamination.
- Interrupted syringe method: All equipment is disposable so less chance of contamination
- When catheters are used, they are sterilized either with ethylene oxide or by color sterilization method. These agents are harmful for embryos. With ethylene oxide it should be sterilized one week before collection and put it in air so that harmful material is decreased. If cold chain is to be used then use normal saline.
- Embryo collection is done in diestrus when cervix is closed but still it is penetratable. A steel rod known as cervix dilator is used. All things sterilize. Pass it slowly that will loosen the rings of cervix, take out dilator and pass the catheter.
- Catheters are not hard enough because they are of rubber. To create stiffness in catheter we pass steel rod in it and after passing we direct it toward one of the horns. Tip of catheter has opening and an area where there is balloon i.e. deflator. Enter N.S so that balloon is flatted. When the balloon is bigger enough to fill the lumen of the uterus the catheter is fixed.
- Now fill the uterus from the opening inside the catheter, the fluid when starts filling in uterus, move the top of horn where the embryos would be and take out the fluid which contains embryos. In first attempt of filling fluid it contains 85 % of embryos. No. of plates are marked. Immediately after the collection, shift the material in lab and then search of embryo.
Evaluation
- Continuity of zona pellucida (zona is double layered and its diameter is 12-15 µm).
- The arrangement of blastomeres in the zona: they should be arranged in circular fashion and no extension of cells from the zona.
- Blastomeres should be of uniform size.
- Presence of degenerative area: If degeneration present it will appear as black area. It is in %age.
- Presence of vacuole.
Transfer of Embryo
- Use 1-2 ml of epidural anesthesia and go for examination of ovary to check on which ovary the CL is present. Transfer of the embryo should be transferred into ipsilateral horn (horn containing CL).
- Ideal site for the deposition or transfer is 5-10 cm above from bifurcation.
- Firstly you have to straighten the horn
